从零实现 LLM Inference:069. Operator Fusion(给 roseinfer 补齐 attention 之外的算子融合)
前面几篇我们把 roseinfer 的 attention 侧补得差不多了:flashinfer prefill、paged attention decode、CUDA graph、chunked prefill、prefix caching……这些都是“没有就很难跟业内对齐”的基础设施。
但真正做过线上推理你会发现:把 attention 做到极致只是上半场。尤其是 decode(T=1) 场景里,很多算子会变成非常刺眼的热点:
- kernel launch 太多(小算子碎片化)
- HBM 带宽浪费(反复读写同一块激活)
- Python/dispatcher 侧开销开始显形(在小 batch / 小 T 里更明显)
这篇我们做两件事:
- 业界调研:vLLM / SGLang / TensorRT-LLM 在 attention 之外 主要怎么做“成熟融合”。
- 落地实现:在
roseinfer加一条可控、可回归、默认开启的融合路径:Triton fused add+LayerNorm(in-place)(并顺手把cuda graph / chunked prefill / paged attention / prefix caching这类业内默认优化改为默认开启,全部都有--no-*开关用于严谨对比)。
业界调研:attention 之外,大家主要融合什么?
1) vLLM:自定义 op + 编译期 pattern fusion(把“残差+norm”当成一等公民)
vLLM 的一个核心工程思想是:把推理中反复出现的“模式”抽出来做 fused op,尤其是:
- residual add + (RMSNorm/LayerNorm)
- RoPE + Q/K norm(更靠近 Llama 系列)
- 某些量化/AllReduce 的融合(TP/EP 场景)
并且它不仅仅“手写 CUDA”,还会在 compilation pass 里做 pattern matcher,把高层图匹配成 fused op(能覆盖更多模型变体)。
2) SGLang:默认打开一揽子推理优化 + 关键热点做融合
SGLang 的风格更偏“系统化默认开”:prefill/decode scheduler、chunked prefill、flashinfer backend、CUDA graph……同时也会在一些模型路径上做融合(例如把某些前处理/后处理变成更少的 kernel)。
3) TensorRT-LLM:引擎化(engine)+ plugin 生态(把融合变成可组合的后端能力)
TensorRT-LLM 的方法论非常直接:能被 TensorRT 编译器吃掉的就让编译器做(层融合、kernel 选择、调度),不能的就用 plugin 补齐:
- GEMM 用 cublasLt / TensorRT tactic
- elementwise/reduction 的关键路径(norm、activation、residual)大量走 fused kernel / plugin
- 配合 IFB(in-flight batching)、paged KV、CUDA graph 等系统优化,做到“默认就很强”
为什么 “residual + LayerNorm” 在 decode(T=1) 会变成大热点?
LayerNorm(对最后一维 $D$)的定义:
\[\mu = \frac{1}{D}\sum_{i=1}^{D} x_i,\quad \sigma^2 = \frac{1}{D}\sum_{i=1}^{D}(x_i-\mu)^2\] \[\mathrm{LN}(x) = \frac{x-\mu}{\sqrt{\sigma^2+\epsilon}}\odot\gamma+\beta\]Transformer block 的常见模式(以 GPT2 为例):
\[x \leftarrow x + \mathrm{Attn}(\mathrm{LN}(x)),\quad x \leftarrow x + \mathrm{MLP}(\mathrm{LN}(x))\]在 decode(T=1) 时,attention/MLP 的 GEMM 变小了,launch + 带宽的占比上升,于是:
x + residual(一次读写)LayerNorm(再读写一次,还要做 reduction)
会变成你在 profiler 里反复看到的“小刀割肉”。
因此业内非常常见的一步是:把它们 fuse 成一个 kernel,直接算:
\[y = \mathrm{LN}(x + r)\]并且很多实现会把 $x\leftarrow x+r$ 原地写回(in-place),减少额外的中间张量与 allocator 压力(对 CUDA graph 也更友好)。
我们的取舍:自写 CUDA vs 开源库 vs torch.compile?
结论先说:
- attention:优先用成熟库(
flashinfer/flash-attn),我们当前默认auto -> flashinfer。 - attention 之外的小算子融合:优先用 Triton 快速落地(可读性好、迭代快、可选依赖),后续再视收益把最热的部分下沉为 CUDA extension。
- torch.compile:更适合“把一串 elementwise 粘起来”或做 pattern-based 替换,但在推理引擎里要同时兼容动态 shape、CUDA graph、外部 custom op(flashinfer)时,需要更谨慎。我们把它作为后续路线,而不是这次的第一落地点。
所以这次我们先把最通用、最稳定、收益最确定的一块做掉:fused add+LayerNorm(in-place)。
我们的实现:Triton fused add+LayerNorm(in-place)+ 默认开关体系
1) 核心融合算子
rosellm/rosetrainer/fused_layernorm.py:实现两个 Triton kernellayer_norm(x, weight, bias):LNadd_layer_norm_(x, residual, weight, bias):把x += residual原地写回,并返回LN(x)
并且做了两层兜底:
- Triton 不可用 / 非 CUDA / 非 contiguous / dtype 不支持:自动 fallback 到
torch.nn.functional.layer_norm(仍保持 in-place 语义) - 训练/有梯度:不走 fused 路径(避免 autograd 语义风险)
2) 模型侧接入(不破坏训练路径)
rosellm/rosetrainer/model.py:- 在
TransformerBlock.forward()里,inference(no_grad) 且use_fused_ops=True时:ln1(x)走 fused LNx + attn_out+ln2走 fused add+LN(in-place)x + mlp_out改为x.add_(mlp_out)(减少一次额外分配)
GPTModel默认ROSELLM_FUSED_OPS=1,并允许被InferenceEngine(use_fused_ops=...)覆盖
- 在
3) Serving 默认开关(对齐“业内默认开”)
把业内常见默认优化直接 default=true,并提供 --no-*:
paged attention:默认开启cuda graph:默认开启(paged decode)chunked prefill:默认开启(需要 CUDA + AMP + flashinfer;否则自动降级关闭)prefix caching:默认开启prefill attention backend:默认auto -> flashinfer/flash-attn/naivefused ops:默认开启(本篇新增)
对应实现主要在:
rosellm/roseinfer/engine.py:默认值与 auto backend 解析;把use_fused_ops下发给 modelrosellm/roseinfer/server.py:补齐--no-*,并做自动降级(例如--no-amp时自动关闭 chunked)
Benchmark:online/offline(固定业内默认优化开启,仅对比 fused ops on/off)
本篇 benchmark 仍然复用 066/067/068 的框架:
- online:TraceA 回放(TTFT/TPOT/ITL/E2E)
- offline:合成 prompt ids 的吞吐(req/s, tok/s)
并新增 --roseinfer-compare-fused-ops,在同一轮 benchmark 里跑两次 roseinfer:
roseinfer:fused ops 开启(默认)roseinfer+nofuse:fused ops 关闭(A/B 对比组)
Online
python benchmarks/serving/online_compare.py \
--model gpt2 --gpu 0 \
--n 100 --max-output-len 64 \
--ignore-eos \
--roseinfer-compare-fused-ops
Offline
python benchmarks/serving/offline_compare.py \
--model gpt2 --gpu 0 \
--num-prompts 128 --input-len 256 --output-len 64 \
--max-batch-size 128 \
--ignore-eos \
--roseinfer-compare-fused-ops
结果(HF GPT-2 / GPU0)
运行环境 / 版本 / 耗时
- versions:
git_rev=f724376, rosellm=0.1.0, torch=2.9.0, transformers=4.57.1, python=3.10.9 - online:
dtype=fp16,ignore_eos=true,n=100,scales=0.4,0.5,0.6,0.7,0.8,1.6, wall=747.34s - offline:
dtype=fp16,ignore_eos=true,num_prompts=128,input_len=256,output_len=64, wall=57.29s
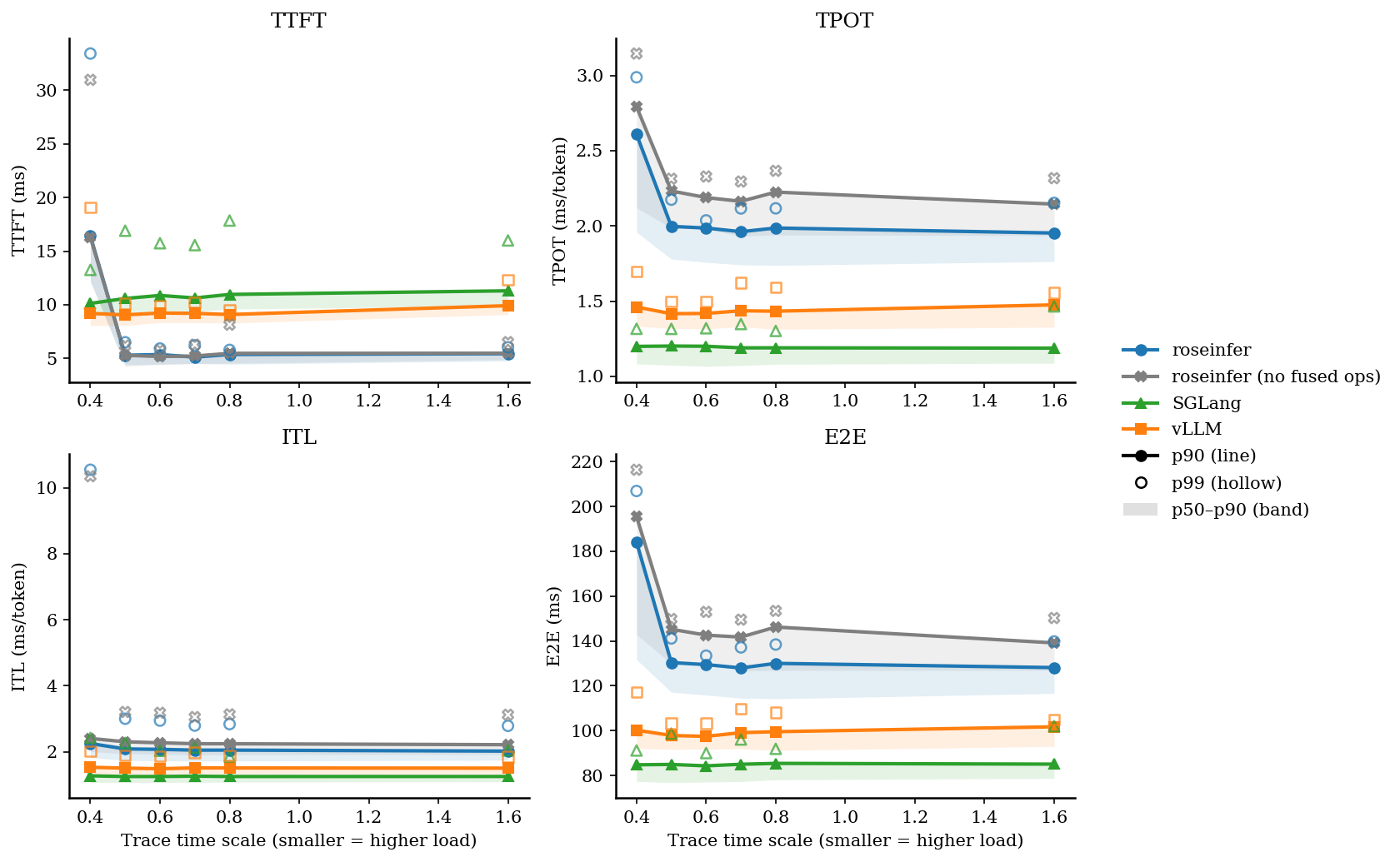
Online:p50/p90/p99(ms)
| scale | backend | TTFT p50/p90/p99 (ms) | TPOT p50/p90/p99 (ms) | ITL p50/p90/p99 (ms) | E2E p50/p90/p99 (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.40 | roseinfer | 12.19/16.41/33.43 | 1.96/2.61/2.99 | 1.82/2.25/10.55 | 131.69/184.12/206.93 |
| 0.40 | roseinfer (no fused ops) | 12.18/16.30/30.97 | 2.12/2.79/3.15 | 2.00/2.40/10.35 | 142.85/195.51/216.40 |
| 0.40 | SGLang | 8.91/10.13/13.25 | 1.08/1.20/1.32 | 1.06/1.27/2.42 | 77.28/84.73/91.11 |
| 0.40 | vLLM | 8.05/9.20/19.08 | 1.33/1.46/1.70 | 1.32/1.53/2.01 | 92.06/100.19/117.21 |
| 0.50 | roseinfer | 4.42/5.29/6.51 | 1.78/2.00/2.17 | 1.73/2.08/3.00 | 117.13/130.35/141.12 |
| 0.50 | roseinfer (no fused ops) | 4.26/5.29/6.21 | 1.99/2.23/2.31 | 1.94/2.30/3.20 | 129.90/145.23/149.80 |
| 0.50 | SGLang | 9.26/10.59/16.91 | 1.07/1.20/1.32 | 1.06/1.25/2.26 | 76.79/84.89/98.66 |
| 0.50 | vLLM | 8.07/9.06/10.12 | 1.32/1.42/1.50 | 1.31/1.50/1.89 | 91.57/97.80/103.30 |
| 0.60 | roseinfer | 4.46/5.36/5.92 | 1.76/1.99/2.04 | 1.72/2.07/2.94 | 115.85/129.43/133.43 |
| 0.60 | roseinfer (no fused ops) | 4.44/5.18/5.74 | 1.98/2.19/2.33 | 1.93/2.27/3.18 | 130.10/142.59/152.97 |
| 0.60 | SGLang | 9.31/10.87/15.74 | 1.07/1.20/1.32 | 1.07/1.25/2.03 | 77.01/84.26/89.95 |
| 0.60 | vLLM | 8.34/9.23/9.87 | 1.32/1.42/1.50 | 1.31/1.48/1.87 | 91.70/97.42/103.19 |
| 0.70 | roseinfer | 4.52/5.12/6.22 | 1.74/1.96/2.12 | 1.71/2.05/2.79 | 114.46/127.95/137.12 |
| 0.70 | roseinfer (no fused ops) | 4.52/5.22/6.28 | 1.93/2.16/2.30 | 1.90/2.24/3.05 | 126.76/141.72/149.51 |
| 0.70 | SGLang | 9.35/10.64/15.56 | 1.07/1.19/1.35 | 1.07/1.26/2.13 | 77.24/84.97/96.02 |
| 0.70 | vLLM | 8.33/9.20/10.21 | 1.33/1.44/1.62 | 1.32/1.51/1.97 | 91.81/99.07/109.83 |
| 0.80 | roseinfer | 4.46/5.37/5.80 | 1.74/1.99/2.12 | 1.72/2.05/2.83 | 114.21/129.99/138.41 |
| 0.80 | roseinfer (no fused ops) | 4.56/5.47/8.15 | 1.94/2.23/2.37 | 1.91/2.24/3.13 | 126.84/146.23/153.41 |
| 0.80 | SGLang | 9.60/10.97/17.85 | 1.08/1.19/1.30 | 1.07/1.25/1.86 | 78.05/85.35/91.85 |
| 0.80 | vLLM | 8.29/9.09/9.55 | 1.31/1.43/1.59 | 1.32/1.50/1.89 | 91.12/99.50/108.08 |
| 1.60 | roseinfer | 4.76/5.44/6.03 | 1.76/1.95/2.15 | 1.74/2.02/2.78 | 116.56/128.12/139.77 |
| 1.60 | roseinfer (no fused ops) | 4.90/5.49/6.52 | 1.94/2.15/2.32 | 1.92/2.21/3.12 | 126.91/139.14/150.24 |
| 1.60 | SGLang | 9.90/11.30/16.00 | 1.09/1.19/1.47 | 1.09/1.25/2.04 | 78.63/85.02/101.98 |
| 1.60 | vLLM | 9.09/9.92/12.33 | 1.33/1.48/1.56 | 1.33/1.50/1.85 | 92.93/101.69/104.96 |
Online:2x2 指标总览图(p90 曲线 + p50~p90 band,空心点为 p99)
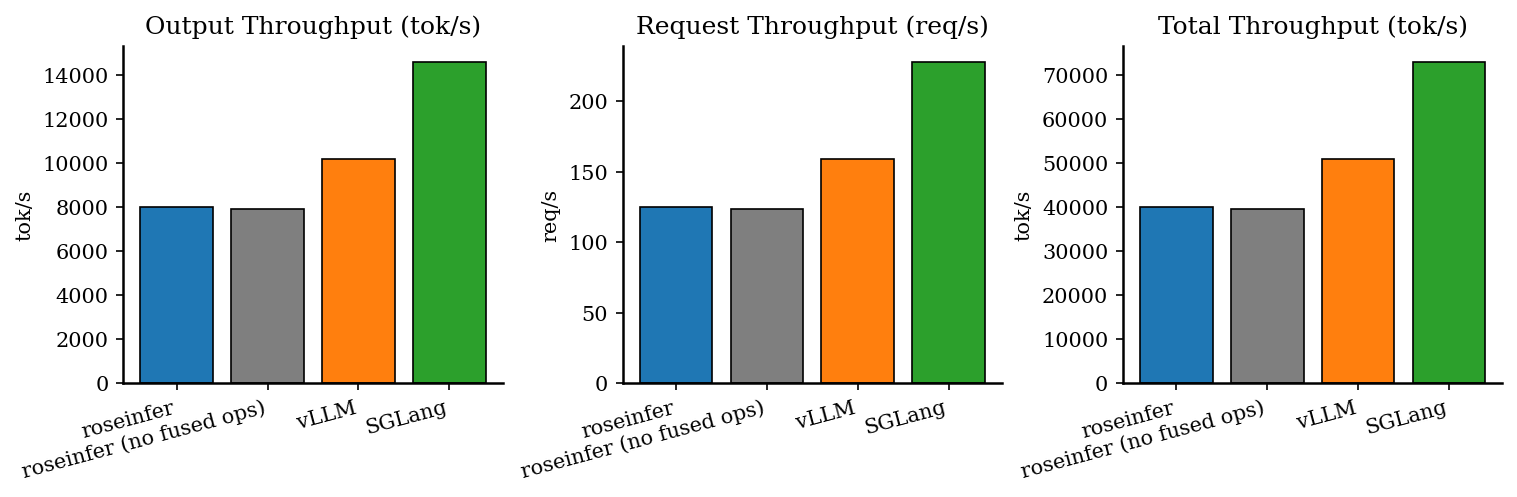
Offline:吞吐对比
| backend | req/s | output tok/s | total tok/s | total latency (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| roseinfer | 124.91 | 7994.05 | 39970.23 | 1.025 |
| roseinfer (no fused ops) | 123.53 | 7905.89 | 39529.44 | 1.036 |
| SGLang | 227.99 | 14591.24 | 72956.19 | 0.561 |
| vLLM | 159.10 | 10182.44 | 50912.22 | 0.805 |
小结 & 下一步
roseinfer现在具备 attention 之外的第一块“成熟融合”能力:fused add+LayerNorm(in-place),默认开启,并可一键--no-fused-ops做严谨 A/B。- 同时把
cuda graph / chunked prefill / paged attention / prefix caching这类业内默认优化都改成默认开启,并补齐--no-*开关与自动降级逻辑,避免用户手动拼参数。 - 下一步如果要继续向 vLLM/TRT-LLM 靠拢,最值得继续做的融合通常是:
- RMSNorm/LN 的更多形态(带 residual / gated / RoPE 前后)
- MLP side 的 epilogue(bias+activation)与更少的中间写回
- 更系统化的 “pattern -> fused op” 编译/替换机制(可选接入 torch.compile 的 pass)